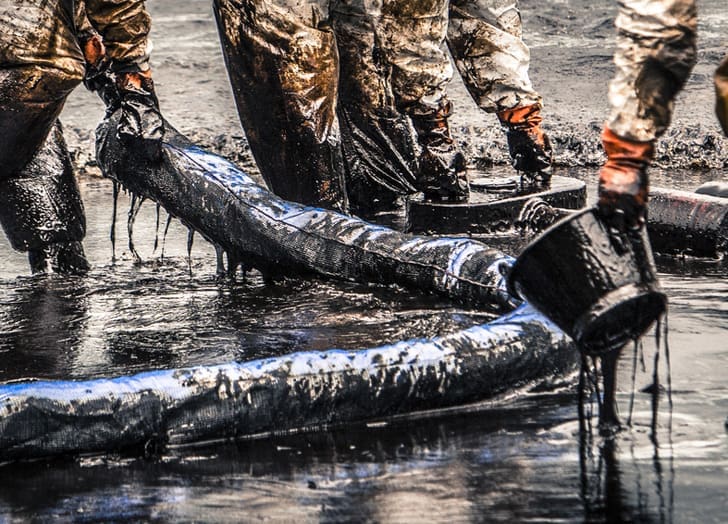
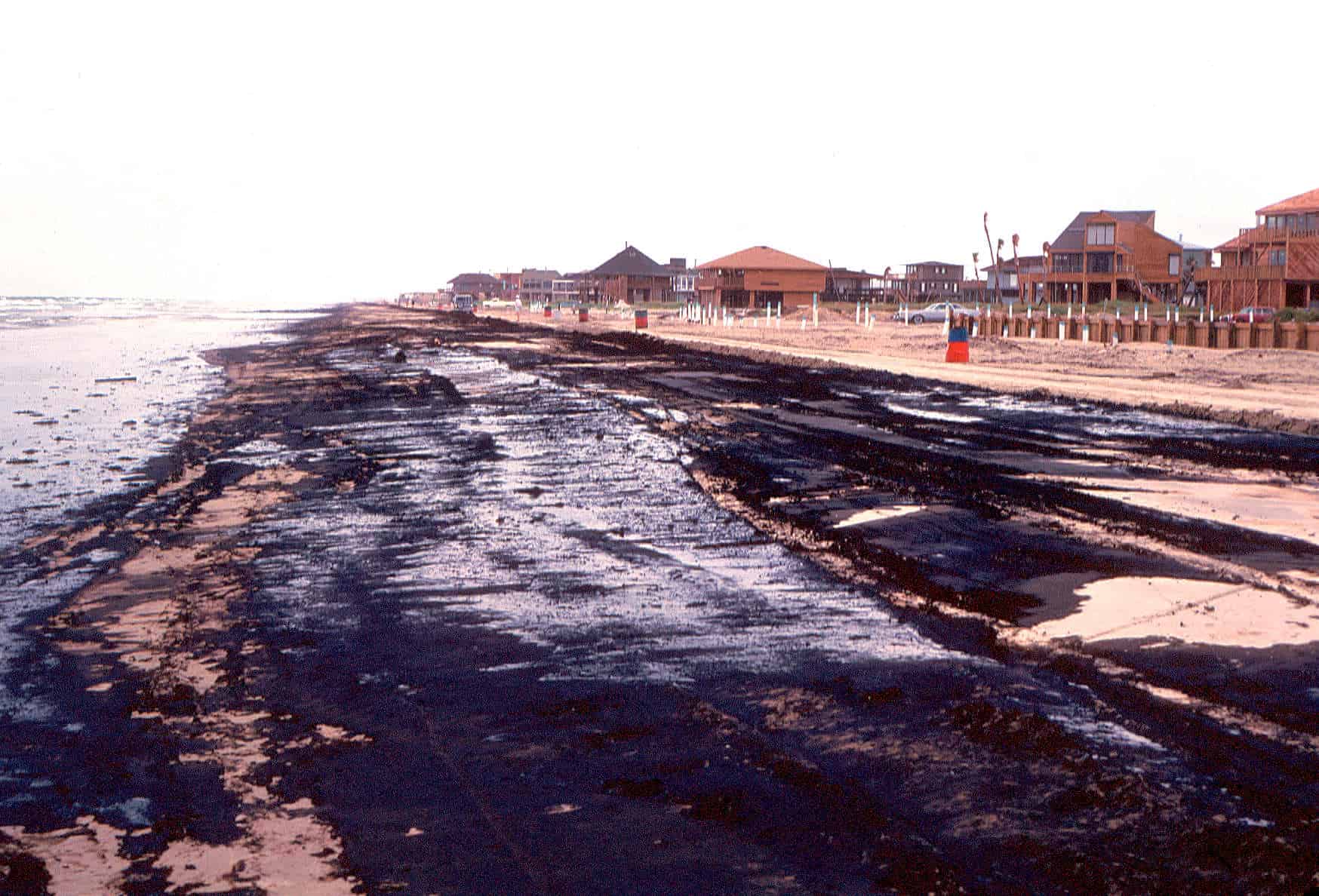
Oil spill dispersants can prevent severe environmental threat, requiring immediate and effective response strategies to minimize their impact. Among the various methods employed for oil spill response, the use of dispersants stands out due to its ability to break down oil into smaller droplets, enhancing natural degradation processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the different types of oil spill dispersants, their mechanisms of action, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for use.
Introduction to Oil Spill Dispersants
Oil spill dispersants are chemical agents specifically formulated to promote the dispersion of oil into the water column, facilitating its biodegradation by natural processes. They work by breaking down the oil slick into smaller droplets, which are more easily biodegraded by naturally occurring microorganisms. The primary goal of using dispersants is to reduce the environmental impact of oil spills, particularly in sensitive areas such as shorelines and marine habitats.
The use of oil spill dispersants is a critical component of oil spill response strategies, particularly in offshore spills where mechanical recovery methods may be less effective due to weather conditions, distance from shore, or the volume of oil released. However, the application of dispersants is a subject of debate and scrutiny due to potential environmental impacts and concerns about their long-term effectiveness.
Mechanism of Action
Oil spill dispersants contain surfactants, which are compounds that reduce the surface tension between oil and water. This reduction in surface tension allows the oil to break up into smaller droplets, which are then dispersed throughout the water column. The surfactants in oil spill dispersants typically consist of two parts: a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and a hydrophobic (oil-attracting) tail. When applied to an oil slick, these molecules align themselves at the oil-water interface, surrounding the oil droplets and preventing them from coalescing.
Types of Oil Spill Dispersants
Oil spill dispersants can be categorized based on their composition and the specific conditions under which they are used. The primary types include:
1. Corexit Dispersants
Corexit dispersants are among the most widely recognized and utilized chemical dispersants. Developed by Nalco Environmental Solutions (now owned by Baker Hughes), Corexit products are composed of surfactants and solvents designed to reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water. This action facilitates the dispersion of oil into smaller droplets that can be more easily degraded by natural processes.
Corexit dispersants have been extensively tested and approved for use by regulatory agencies, including the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). They are effective across a wide range of crude oils and can be applied under various environmental conditions. However, concerns have been raised regarding their potential toxicity to marine life and long-term environmental impacts, particularly when used in large quantities or in sensitive ecosystems.
2. Synthetic Dispersants
Synthetic dispersants are chemical formulations designed specifically for breaking down oil slicks. These dispersants often contain proprietary blends of surfactants, solvents, and additives that enhance their effectiveness in differentiating oil from water and promoting dispersion. Synthetic dispersants may offer advantages such as rapid action and compatibility with a broad spectrum of oil types and environmental conditions.
The formulation of synthetic dispersants allows for customization based on the characteristics of the oil spill and the desired environmental outcomes. However, like Corexit dispersants, their use requires careful assessment of potential ecological impacts and adherence to regulatory guidelines. Research continues to focus on improving the efficacy and environmental safety of synthetic dispersants through ongoing testing and development.
3. Bioremediation Agents
Bioremediation agents represent a newer approach to oil spill dispersants for cleanup, focusing on biological processes to degrade oil rather than purely chemical dispersion. These agents often include nutrients and microbial additives that stimulate the growth of oil-degrading bacteria and fungi. Bioremediation can be applied in conjunction with dispersants or as a standalone treatment, depending on the characteristics of the oil spill dispersants and environmental conditions.
The effectiveness of bioremediation oil spill dispersant agents relies on the presence of suitable microorganisms capable of metabolizing hydrocarbons present in crude oil. This method promotes natural degradation processes and can be particularly beneficial in environments where microbial activity is abundant, such as coastal waters and wetlands. However, the application of bioremediation agents requires careful monitoring to ensure that they do not introduce harmful pathogens or disrupt existing ecosystems.
Mechanisms of Action

Oil spill dispersants work through several key mechanisms to break down oil and facilitate its dispersion:
- Surfactant Action: Dispersants contain surfactants that lower the surface tension between oil and water, allowing oil to break up into smaller droplets.
- Emulsification: Dispersants emulsify oil into micron-sized droplets that disperse more readily throughout the water column.
- Enhanced Biodegradation: By increasing the surface area of oil exposed to microbial activity, dispersants accelerate natural biodegradation processes.
- Physical Dispersion: Dispersants help prevent oil from forming thick surface slicks, reducing the likelihood of oil reaching shorelines and sensitive habitats.
Effectiveness and Limitations
The effectiveness of oil spill dispersants depends on several factors, including:
- Oil Type: Different crude oils have varying viscosities and chemical compositions, influencing how effectively dispersants break them down.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors such as water temperature, wave action, and salinity can affect dispersant performance and the behavior of dispersed oil.
- Application Timing: Oil spill dispersants are most effective when applied early after a spill, before oil spreads and weathers.
- Dispersant Formulation: The specific composition of dispersants, including surfactant types and solvent concentrations, can impact their effectiveness under different conditions.
While oil spill dispersants can mitigate the immediate impacts of oil spills, they also have limitations and potential drawbacks:
- Toxicity Concerns: Some dispersants and their breakdown products may be toxic to marine organisms, raising concerns about long-term environmental impacts.
- Effectiveness in Deepwater: Dispersants may be less effective in deepwater environments, where achieving thorough mixing and dispersion can be challenging.
- Regulatory Constraints: The use of dispersants is regulated by national and international authorities to minimize environmental risks and ensure proper application protocols.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of oil spill dispersants is a subject of ongoing research and debate within the scientific community and regulatory agencies. Key considerations include:
- Ecotoxicity: Dispersants and their breakdown products can potentially harm marine organisms, particularly fish, shellfish, and plankton.
- Bioaccumulation: Toxic components of dispersants may bioaccumulate in the food chain, posing risks to higher trophic levels.
- Long-Term Effects: The ecological consequences of dispersant use may persist beyond the initial cleanup phase, affecting marine ecosystems and biodiversity.
Regulatory Framework
The use of oil spill dispersants is subject to strict regulatory oversight to minimize environmental risks and ensure safe application. Regulatory frameworks vary by country but generally include:
- Approval and Testing: Dispersants must undergo rigorous testing and evaluation to assess their effectiveness and environmental safety before receiving regulatory approval.
- Application Guidelines: Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on the proper use of dispersants, including application rates, application methods, and monitoring requirements.
- Emergency Response Plans: Oil spill response plans mandated by regulatory agencies outline procedures for dispersant use in emergency situations, emphasizing safety and environmental protection.
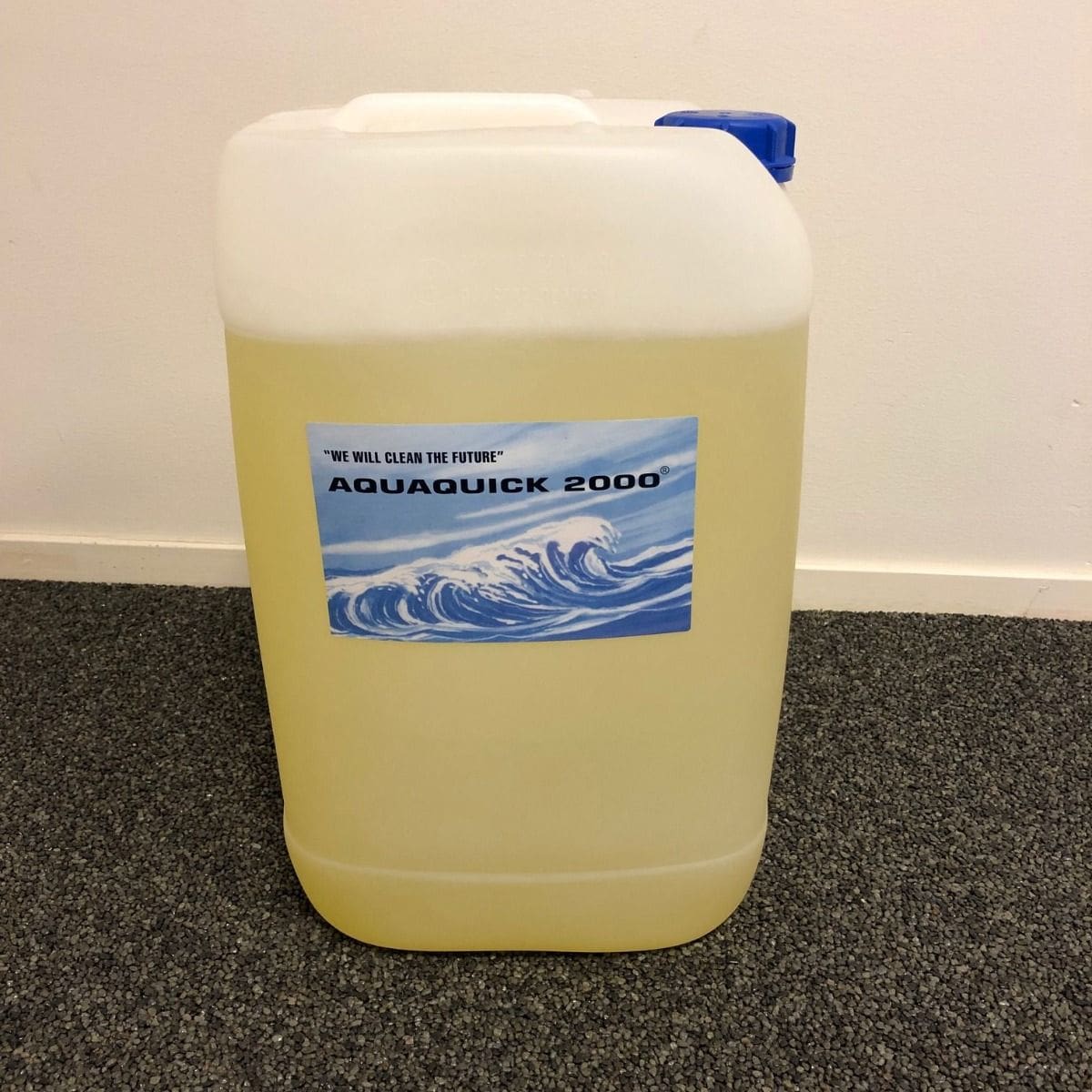
AQUAQUICK 2000: Advanced Oil Spill Dispersants
AQUAQUICK 2000 represents a significant advancement in the field of oil spill response and cleanup. Developed by AQUAQUICK Global B.V., this innovative dispersant offers a sustainable and effective solution for mitigating the environmental impact of oil spills. This article explores the unique characteristics, mechanisms of action, applications, environmental considerations, and regulatory aspects of AQUAQUICK 2000 in oil spill response.
Introduction to AQUAQUICK 2000
AQUAQUICK 2000 is a specialized oil spill dispersant designed to facilitate the rapid and effective cleanup of oil spills in marine and industrial environments. Unlike traditional dispersants that rely on chemical surfactants and solvents, AQUAQUICK 2000 utilizes a proprietary blend of biodegradable surfactants and natural ingredients. This composition enhances its ability to emulsify and disperse oil into smaller droplets, facilitating its breakdown by natural microbial processes.
The formulation of AQUAQUICK 2000 emphasizes environmental safety and sustainability, making it suitable for use in sensitive ecosystems such as coastal waters, estuaries, and wetlands. Its biodegradable components minimize ecological risks and ensure that residual dispersant and oil breakdown products do not persist in the environment long-term.
Mechanism of Action

AQUAQUICK 2000 works through a multi-faceted mechanism to effectively disperse and biodegrade oil spilled in water:
- Surfactant Activity: The dispersant contains surfactants that lower the surface tension between oil and water, allowing the oil to break up into smaller droplets.
- Emulsification: By emulsifying oil into micron-sized droplets, AQUAQUICK 2000 enhances its dispersion throughout the water column. This dispersion prevents the formation of large surface slicks and facilitates the exposure of oil to natural microbial communities.
- Biodegradation Enhancement: The dispersant accelerates the natural biodegradation of oil by increasing its surface area and accessibility to oil-degrading microorganisms. These microorganisms metabolize the oil droplets, converting them into less harmful substances such as carbon dioxide and water.
Applications of AQUAQUICK 2000
AQUAQUICK 2000 is applied in response to oil spills through various methods tailored to the specific spill scenario:
- Aerial Application: The dispersant can be sprayed from aircraft onto oil slicks on water surfaces, facilitating rapid dispersion and degradation of spilled oil.
- Vessel-Mounted Spraying: Response vessels equipped with spraying equipment apply AQUAQUICK 2000 directly onto oil slicks, ensuring localized treatment and containment of spills.
- Surface Washing: In cases where oil has reached shorelines or man-made structures, AQUAQUICK 2000 can be applied using pressure washing or manual application methods. This approach helps remove oil residues and facilitates cleanup efforts in affected areas.
- In-Situ Treatment: AQUAQUICK 2000 can also be used for in-situ treatment of contaminated water bodies, where it acts to disperse and degrade oil while minimizing environmental impacts.
Environmental Considerations for Oil Spill Dispersants
AQUAQUICK 2000 is formulated with a strong emphasis on environmental safety and sustainability:
- Biodegradability: The dispersant’s biodegradable surfactants and natural ingredients ensure that it breaks down into non-toxic byproducts over time, reducing ecological risks.
- Non-Toxicity: Unlike some conventional dispersants that may contain harmful chemicals, AQUAQUICK 2000 is designed to have minimal impact on marine life and ecosystems.
- Ecosystem Compatibility: The formulation of AQUAQUICK 2000 makes it suitable for use in diverse ecosystems, including coastal areas, estuaries, and freshwater habitats.
- Long-Term Effects: Studies indicate that AQUAQUICK 2000 does not leave persistent residues or harmful substances in the environment, supporting its use in environmentally sensitive areas.
Effectiveness and Benefits of Oil Spill Dispersants
AQUAQUICK 2000 offers several advantages over traditional oil spill dispersants:
- Rapid Action: The dispersant quickly emulsifies and disperses oil, reducing the potential for large-scale oil slicks and minimizing the spread of contamination.
- Versatility: It is effective across a wide range of crude oils and petroleum products, making it a versatile tool for various spill scenarios.
- Safety: AQUAQUICK 2000’s non-toxic formulation enhances safety for cleanup personnel and reduces risks to marine life and ecosystems.
- Compatibility with Bioremediation: The dispersant enhances natural biodegradation processes, supporting ecosystem recovery and restoration after spills.
Regulatory Framework of Oil Spill Dispersants
The use of AQUAQUICK 2000 is governed by regulatory frameworks aimed at ensuring safe and effective oil spill response:
- Regulatory Approval: The dispersant undergoes rigorous testing and evaluation to meet regulatory standards for effectiveness, environmental safety, and human health.
- Application Guidelines: Regulatory agencies provide guidelines on the proper use, handling, and disposal of AQUAQUICK 2000 during oil spill response operations.
- Emergency Response Plans: Oil spill response plans mandated by regulatory agencies include provisions for the use of dispersants like AQUAQUICK 2000, outlining protocols for application, monitoring, and assessment.
AQUAQUICK 2000 represents a significant innovation in oil spill dispersants, combining effective cleanup capabilities with environmental safety and sustainability. Its biodegradable formulation and ability to enhance natural oil degradation processes make it a valuable tool for mitigating the impact of oil spills on marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
As the industry continues to prioritize environmental stewardship and sustainability, AQUAQUICK 2000 exemplifies a responsible approach to oil spill response and environmental protection, ensuring the preservation of natural resources and habitats for future generations. Continued research and development will further enhance the effectiveness and safety of dispersants like AQUAQUICK 2000, advancing our ability to respond to oil spills while minimizing ecological impacts.
Conclusion
Oil spill dispersants play a critical role in mitigating the environmental impact of oil spills by accelerating the natural breakdown of oil and preventing its spread to sensitive habitats. Understanding the types, mechanisms, effectiveness, and environmental considerations of dispersants is essential for developing and implementing effective spill response strategies. Continued research and innovation are necessary to improve dispersant technologies, enhance environmental safety, and minimize ecological impacts in the event of future oil spills. Regulatory agencies, industry stakeholders, and environmental organizations play pivotal roles in ensuring responsible dispersant use and advancing sustainable practices for oil spill response and cleanup.














